Biological molecules
All molecules found within living things can be grouped into one of three categories: carbohydrates, proteins and lipids. They are comprised of long chains which are broken down into simpler subunits during digestion.
Carbohydrates
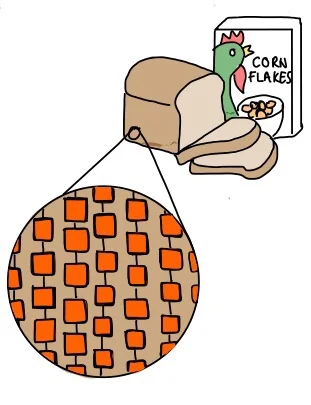
Foods such as bread, cereal and potato contains a high proportion of carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are made up of sugar molecules joined together in long chains. A single sugar is called a monosaccharide and two sugar molecules bonded together is a disaccharide. For example, sucrose is a disaccharide as it consists of two monosaccharides (glucose and fructose) bonded together. Several sugars joined together in one long chain is referred to as a polysaccharide. Examples of polysaccharides include cellulose, starch and glycogen.
Sugar molecules contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
Proteins
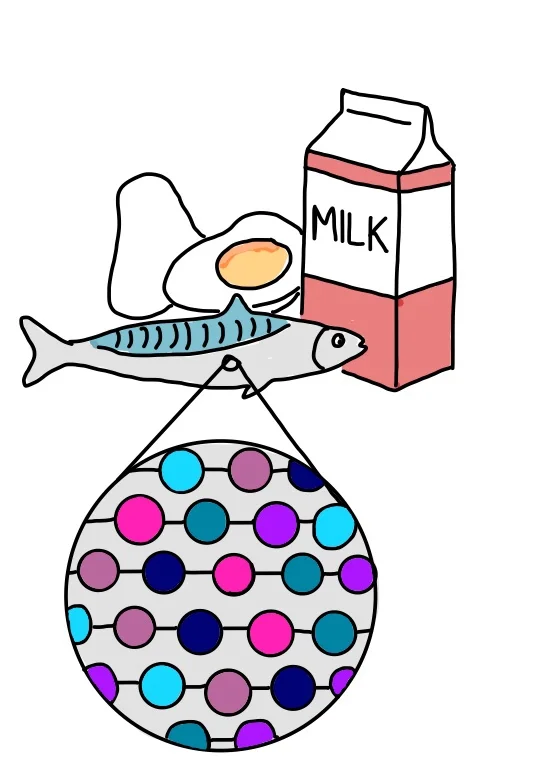
Proteins are one of the most abundant molecules in our body and make up important cell components, such as enzymes, hormones and antibodies. They are basically long chains of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds. Two amino acids joined together is called a dipeptide whereas long chains of amino acids are called polypeptides.
Amino acids contain atoms of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. Protein-rich sources include meat, fish and beans.
Lipids (triglycerides)
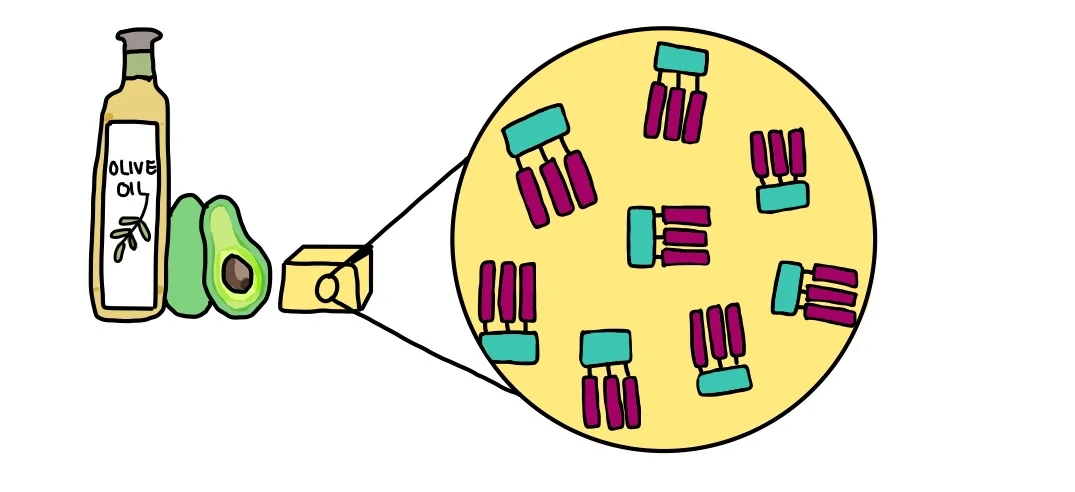
Lipids are important molecules in our body as they store energy, provide insulation and make up cell membranes. Triglycerides are a type of lipid and consist of a glycerol molecule and three fatty acids bonded together.
Lipids contain atoms of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Foods with a high lipid content include butter, oils, nuts and avocado.
Tests for carbohydrates, proteins and lipids
Starch can be detected using iodine solution.
Benedict’s reagent is used to test for the presence of glucose. A colour change from blue to orange/red occurs if glucose is present.
Iodine solution is used to test for starch. Iodine changes from yellow/brown to a blue/black colour if starch is present.
Biuret reagent is used to test for protein and will turn purple if protein is present.
The emulsion test is used to detect the presence of lipids. Ethanol is added to the sample, along with an equal volume of water. If lipid is present a milky-white emulsion will appear.