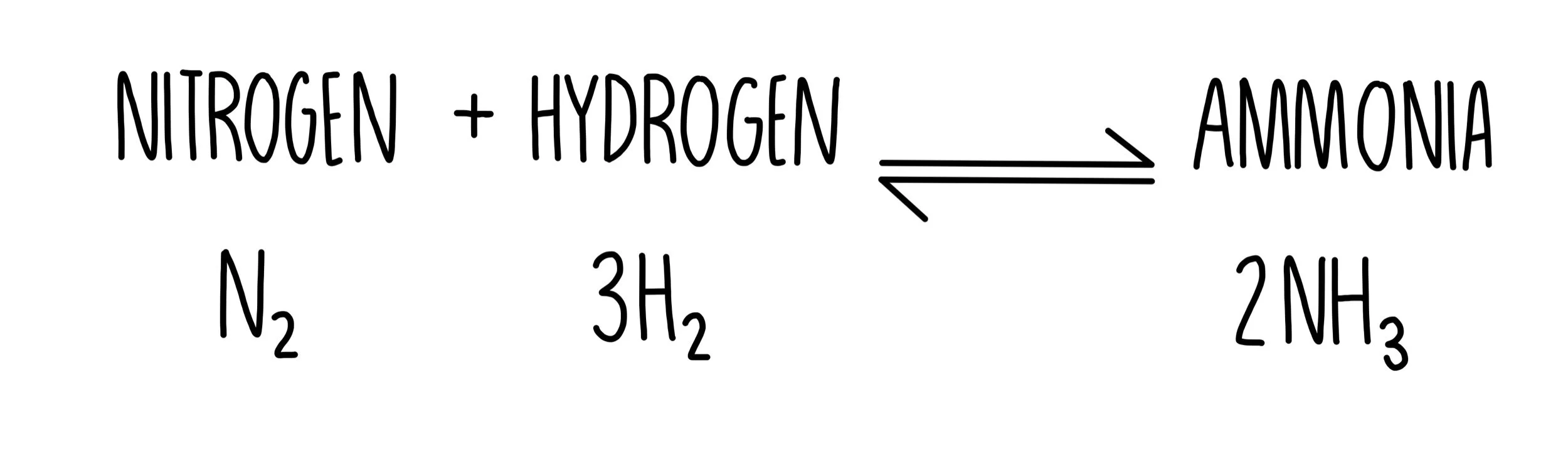Reversible Reactions and Equilibria
Describe what happens to the appearance of anhydrous copper sulfate when water is added.
Anhydrous means ‘without water’. Dry copper sulfate is a white solid but it will turn blue when water is added, forming crystals of hydrated copper sulfate.
Describe the characteristics of a reaction which has reached dynamic equilibrium.
Reactions which have reached dynamic equilibrium have the following characteristics:
The forward and reverse reactions are still happening
The rate of the forward and reverse reactions is the same
The concentrations of the reactants and products remains constant
The equation below shows the Haber process which is used to produce ammonia.
What conditions will increase the yield of ammonia?
Concentration: increasing the concentration of either of the two reactants (nitrogen or hydrogen) will causes the position of equilibrium to shift to the right and favour the yield of ammonia
Pressure: an increase in pressure favours the side with the fewest gas molecules. In this case, ammonia is on the side with the fewest gas molecules, so we need to increase the pressure to increase the yield of ammonia.
Temperature: the forward reaction is exothermic so we need to lower the temperature to increase the yield of ammonia (remember that higher temperatures will favour the endothermic direction).
So the conditions needed are: high concentrations of nitrogen and hydrogen, high pressure and low temperatures.
In reality, less extreme conditions are used. Explain why.
Even though low temperatures will produce a high yield of ammonia, it will result in a slow reaction rate and will be time-consuming (remember that yield and reaction rate are two different things).
Generating high pressures can be expensive and possibly dangerous to staff working near the equipment.
What effect will a catalyst have on the yield of ammonia produced?
This is a bit of a trick question. A catalyst won’t have any effect on equilibrium yield. A catalyst only speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction. Since it speeds up the rate of the forward and reverse reactions by the same amount, the position of equilibrium remains the same.
If the forward reaction is exothermic, what can be deduced about the reverse reaction?
If a reaction is exothermic in the forward direction, this means that it will be endothermic in the reverse direction.